
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Cardiovascular Risk/Epidemiology
- Psychotic Disorders and the Risk of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus, Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Diseases, and All-Cause Mortality: A Population-Based Matched Cohort Study
- You-Bin Lee, Hyewon Kim, Jungkuk Lee, Dongwoo Kang, Gyuri Kim, Sang-Man Jin, Jae Hyeon Kim, Hong Jin Jeon, Kyu Yeon Hur
- Diabetes Metab J. 2024;48(1):122-133. Published online January 3, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0431
- 1,113 View
- 144 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
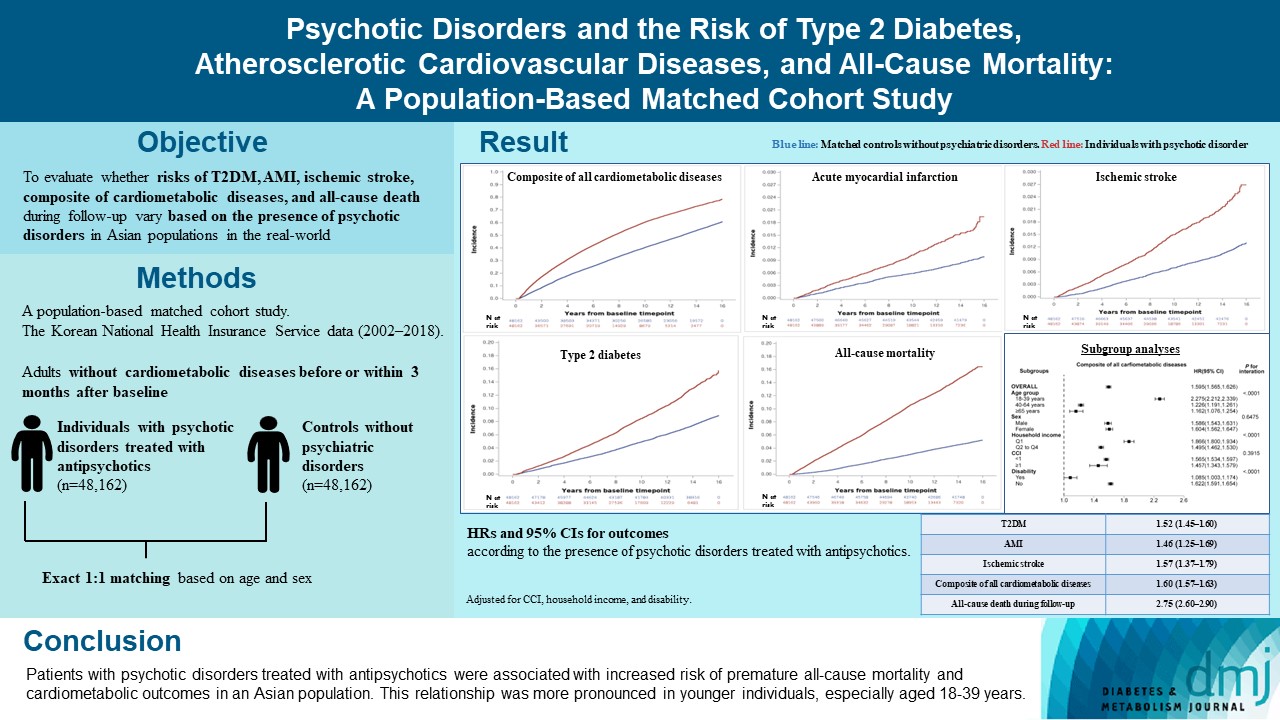
The effects of psychotic disorders on cardiometabolic diseases and premature death need to be determined in Asian populations.
Methods
In this population-based matched cohort study, the Korean National Health Insurance Service database (2002 to 2018) was used. The risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), acute myocardial infarction (AMI), ischemic stroke, composite of all cardiometabolic diseases, and all-cause death during follow-up was compared between individuals with psychotic disorders treated with antipsychotics (n=48,162) and 1:1 matched controls without psychiatric disorders among adults without cardiometabolic diseases before or within 3 months after baseline.
Results
In this cohort, 53,683 composite cases of all cardiometabolic diseases (during median 7.38 years), 899 AMI, and 1,216 ischemic stroke cases (during median 14.14 years), 7,686 T2DM cases (during median 13.26 years), and 7,092 deaths (during median 14.23 years) occurred. The risk of all outcomes was higher in subjects with psychotic disorders than matched controls (adjusted hazard ratios [95% confidence intervals]: 1.522 [1.446 to 1.602] for T2DM; 1.455 [1.251 to 1.693] for AMI; 1.568 [1.373 to 1.790] for ischemic stroke; 1.595 [1.565 to 1.626] for composite of all cardiometabolic diseases; and 2.747 [2.599 to 2.904] for all-cause mortality) during follow-up. Similar patterns of associations were maintained in subgroup analyses but more prominent in younger individuals (P for interaction <0.0001) when categorized as those aged 18–39, 40–64, or ≥65 years.
Conclusion
Patients with psychotic disorders treated with antipsychotics were associated with increased risk of premature allcause mortality and cardiometabolic outcomes in an Asian population. This relationship was more pronounced in younger individuals, especially aged 18 to 39 years.
- Complications
- Association of Muscle Mass Loss with Diabetes Development in Liver Transplantation Recipients
- Sejeong Lee, Minyoung Lee, Young-Eun Kim, Hae Kyung Kim, Sook Jung Lee, Jiwon Kim, Yurim Yang, Chul Hoon Kim, Hyangkyu Lee, Dong Jin Joo, Myoung Soo Kim, Eun Seok Kang
- Diabetes Metab J. 2024;48(1):146-156. Published online January 3, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0100
- 945 View
- 120 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
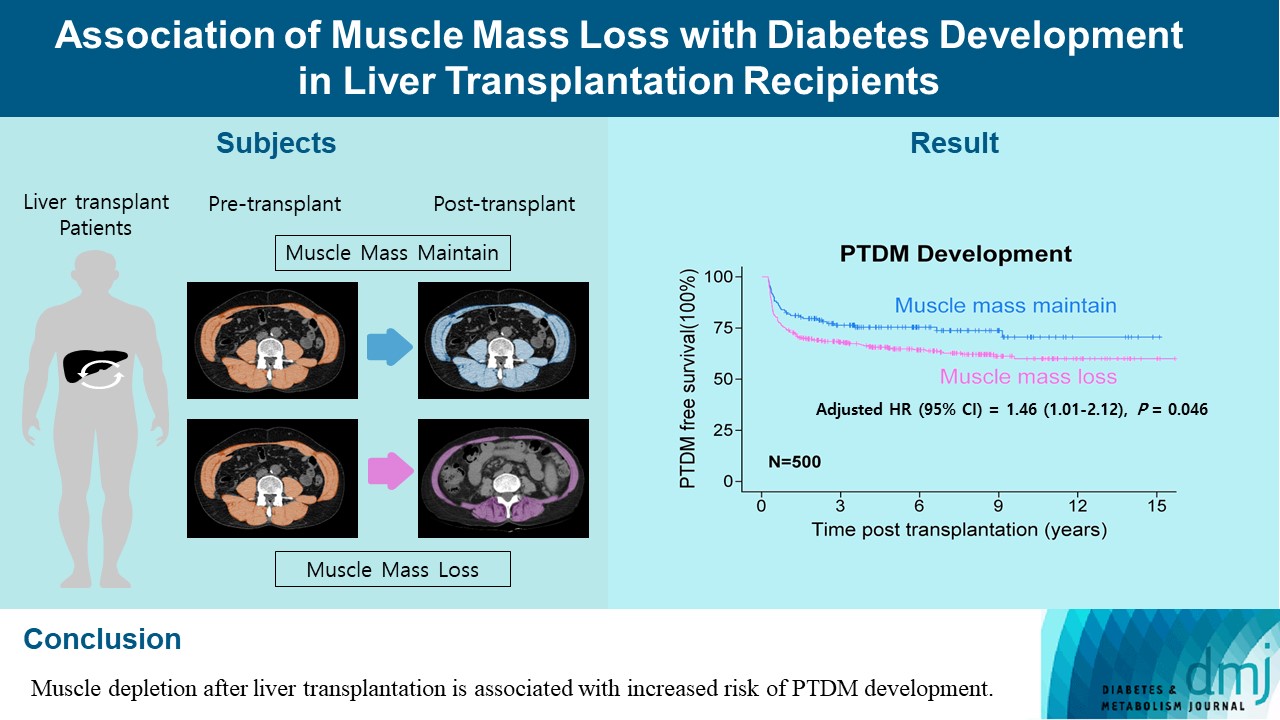
Post-transplant diabetes mellitus (PTDM) is one of the most significant complications after transplantation. Patients with end-stage liver diseases requiring transplantation are prone to sarcopenia, but the association between sarcopenia and PTDM remains to be elucidated. We aimed to investigate the effect of postoperative muscle mass loss on PTDM development.
Methods
A total of 500 patients who underwent liver transplantation at a tertiary care hospital between 2005 and 2020 were included. Skeletal muscle area at the level of the L3–L5 vertebrae was measured using computed tomography scans performed before and 1 year after the transplantation. The associations between the change in the muscle area after the transplantation and the incidence of PTDM was investigated using a Cox proportional hazard model.
Results
During the follow-up period (median, 4.9 years), PTDM occurred in 165 patients (33%). The muscle mass loss was greater in patients who developed PTDM than in those without PTDM. Muscle depletion significantly increased risk of developing PTDM after adjustment for other confounding factors (hazard ratio, 1.50; 95% confidence interval, 1.23 to 1.84; P=0.001). Of the 357 subjects who had muscle mass loss, 124 (34.7%) developed PTDM, whereas of the 143 patients in the muscle mass maintenance group, 41 (28.7%) developed PTDM. The cumulative incidence of PTDM was significantly higher in patients with muscle loss than in patients without muscle loss (P=0.034).
Conclusion
Muscle depletion after liver transplantation is associated with increased risk of PTDM development.
- Others
- Development of Various Diabetes Prediction Models Using Machine Learning Techniques
- Juyoung Shin, Jaewon Kim, Chanjung Lee, Joon Young Yoon, Seyeon Kim, Seungjae Song, Hun-Sung Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(4):650-657. Published online March 11, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0115
- 4,819 View
- 294 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
There are many models for predicting diabetes mellitus (DM), but their clinical implication remains vague. Therefore, we aimed to create various DM prediction models using easily accessible health screening test parameters.
Methods
Two sets of variables were used to develop eight DM prediction models. One set comprised 62 easily accessible examination results of commonly used variables from a tertiary university hospital. The second set comprised 27 of the 62 variables included in the national routine health checkups. Gradient boosting and random forest algorithms were used to develop the models. Internal validation was performed using the stratified 10-fold cross-validation method.
Results
The area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (ROC-AUC) for the 62-variable DM model making 12-month predictions for subjects without diabetes was the largest (0.928) among those of the eight DM prediction models. The ROC-AUC dropped by more than 0.04 when training with the simplified 27-variable set but still showed fairly good performance with ROC-AUCs between 0.842 and 0.880. The accuracy was up to 11.5% higher (from 0.807 to 0.714) when fasting glucose was included.
Conclusion
We created easily applicable diabetes prediction models that deliver good performance using parameters commonly assessed during tertiary university hospital and national routine health checkups. We plan to perform prospective external validation, hoping that the developed DM prediction models will be widely used in clinical practice. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Predictive modeling for the development of diabetes mellitus using key factors in various machine learning approaches
Marenao Tanaka, Yukinori Akiyama, Kazuma Mori, Itaru Hosaka, Kenichi Kato, Keisuke Endo, Toshifumi Ogawa, Tatsuya Sato, Toru Suzuki, Toshiyuki Yano, Hirofumi Ohnishi, Nagisa Hanawa, Masato Furuhashi
Diabetes Epidemiology and Management.2024; 13: 100191. CrossRef - Validation of the Framingham Diabetes Risk Model Using Community-Based KoGES Data
Hye Ah Lee, Hyesook Park, Young Sun Hong
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Integrated Embedded system for detecting diabetes mellitus using various machine learning techniques
Rishita Konda, Anuraag Ramineni, Jayashree J, Niharika Singavajhala, Sai Akshaj Vanka
EAI Endorsed Transactions on Pervasive Health and Technology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The Present and Future of Artificial Intelligence-Based Medical Image in Diabetes Mellitus: Focus on Analytical Methods and Limitations of Clinical Use
Ji-Won Chun, Hun-Sung Kim
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Machine learning for predicting diabetic metabolism in the Indian population using polar metabolomic and lipidomic features
Nikita Jain, Bhaumik Patel, Manjesh Hanawal, Anurag R. Lila, Saba Memon, Tushar Bandgar, Ashutosh Kumar
Metabolomics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Retrospective cohort analysis comparing changes in blood glucose level and body composition according to changes in thyroid‐stimulating hormone level
Hyunah Kim, Da Young Jung, Seung‐Hwan Lee, Jae‐Hyoung Cho, Hyeon Woo Yim, Hun‐Sung Kim
Journal of Diabetes.2022; 14(9): 620. CrossRef - Improving Machine Learning Diabetes Prediction Models for the Utmost Clinical Effectiveness
Juyoung Shin, Joonyub Lee, Taehoon Ko, Kanghyuck Lee, Yera Choi, Hun-Sung Kim
Journal of Personalized Medicine.2022; 12(11): 1899. CrossRef
- Predictive modeling for the development of diabetes mellitus using key factors in various machine learning approaches
- Basic Research
- Differentiation of Microencapsulated Neonatal Porcine Pancreatic Cell Clusters in Vitro Improves Transplant Efficacy in Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus Mice
- Gyeong-Jin Cheon, Heon-Seok Park, Eun-Young Lee, Min Jung Kim, Young-Hye You, Marie Rhee, Ji-Won Kim, Kun-Ho Yoon
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(5):677-688. Published online February 7, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0202
- 4,536 View
- 252 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Neonatal porcine pancreatic cell clusters (NPCCs) have been proposed as an alternative source of β cells for islet transplantation because of their low cost and growth potential after transplantation. However, the delayed glucose lowering effect due to the immaturity of NPCCs and immunologic rejection remain as a barrier to NPCC’s clinical application. Here, we demonstrate accelerated differentiation and immune-tolerant NPCCs by in vitro chemical treatment and microencapsulation.
Methods
NPCCs isolated from 3-day-old piglets were cultured in F-10 media and then microencapsulated with alginate on day 5. Differentiation of NPCCs is facilitated by media supplemented with activin receptor-like kinase 5 inhibitor II, triiodothyronine and exendin-4 for 2 weeks. Marginal number of microencapsulated NPCCs to cure diabetes with and without differentiation were transplanted into diabetic mice and observed for 8 weeks.
Results
The proportion of insulin-positive cells and insulin mRNA levels of NPCCs were significantly increased in vitro in the differentiated group compared with the undifferentiated group. Blood glucose levels decreased eventually after transplantation of microencapsulated NPCCs in diabetic mice and normalized after 7 weeks in the differentiated group. In addition, the differentiated group showed nearly normal glucose tolerance at 8 weeks after transplantation. In contrast, neither blood glucose levels nor glucose tolerance were improved in the undifferentiated group. Retrieved graft in the differentiated group showed greater insulin response to high glucose compared with the undifferentiated group.
Conclusion
in vitro differentiation of microencapsulated immature NPCCs increased the proportion of insulin-positive cells and improved transplant efficacy in diabetic mice without immune rejection. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Dual-targeted nano-encapsulation of neonatal porcine islet-like cell clusters with triiodothyronine-loaded bifunctional polymersomes
Sang Hoon Lee, Minse Kim, Eun-Jin Lee, Sun Mi Ahn, Yu-Rim Ahn, Jaewon Choi, Jung-Taek Kang, Hyun-Ouk Kim
Discover Nano.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Long‐term efficacy of encapsulated xenogeneic islet transplantation: Impact of encapsulation techniques and donor genetic traits
Heon‐Seok Park, Eun Young Lee, Young‐Hye You, Marie Rhee, Jong‐Min Kim, Seong‐Soo Hwang, Poong‐Yeon Lee
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- Dual-targeted nano-encapsulation of neonatal porcine islet-like cell clusters with triiodothyronine-loaded bifunctional polymersomes
- Basic Research
- GPR40 Agonism Modulates Inflammatory Reactions in Vascular Endothelial Cells
- Joo Won Kim, Eun Roh, Kyung Mook Choi, Hye Jin Yoo, Hwan-Jin Hwang, Sei Hyun Baik
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(3):506-511. Published online January 24, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0092
- 4,746 View
- 229 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
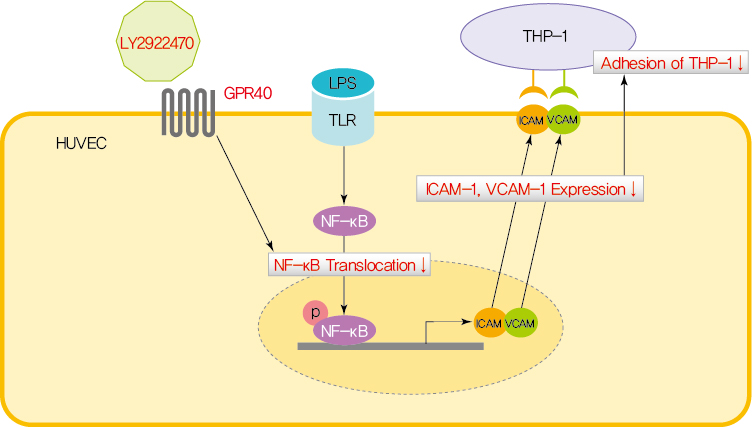
ePub - Endothelial dysfunction is strongly linked with inflammatory responses, which can impact cardiovascular disease. Recently, G protein-coupled receptor 40 (GPR40) has been investigated as a modulator of metabolic stress; however, the function of GPR40 in vascular endothelial cells has not been reported. We analyzed whether treatment of GPR40-specific agonists modulated the inflammatory responses in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs). Treatment with LY2922470, a GPR40 agonist, significantly reduced lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-mediated nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) phosphorylation and movement into the nucleus from the cytosol. However, treatment with another GPR40 agonist, TAK875, did not inhibit LPS-induced NF-κB activation. LPS treatment induced expression of adhesion molecules vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1) and intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) and attachment of THP-1 cells to HUVECs, which were all decreased by LY2922470 but not TAK875. Our results showed that ligand-dependent agonism of GPR40 is a promising therapeutic target for overcoming inflammatory reactions in the endothelium.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Synthetic GPR40/FFAR1 agonists: An exhaustive survey on the most recent chemical classes and their structure-activity relationships
Abhik Paul, Sourin Nahar, Pankaj Nahata, Arnab Sarkar, Avik Maji, Ajeya Samanta, Sanmoy Karmakar, Tapan Kumar Maity
European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry.2024; 264: 115990. CrossRef - Metabolite-sensing GPCRs in rheumatoid arthritis
Xuezhi Yang, Wankang Zhang, Luping Wang, Yingjie Zhao, Wei Wei
Trends in Pharmacological Sciences.2024; 45(2): 118. CrossRef - GPR40 deficiency worsens metabolic syndrome‐associated periodontitis in mice
Yanchun Li, Zhongyang Lu, Cameron L. Kirkwood, Keith L. Kirkwood, Stephen A. Wank, Ai‐Jun Li, Maria F. Lopes‐Virella, Yan Huang
Journal of Periodontal Research.2023; 58(3): 575. CrossRef - Signaling pathways and intervention for therapy of type 2 diabetes mellitus
Rong Cao, Huimin Tian, Yu Zhang, Geng Liu, Haixia Xu, Guocheng Rao, Yan Tian, Xianghui Fu
MedComm.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - G Protein-Coupled Receptor 40 Agonist LY2922470 Alleviates Ischemic-Stroke-Induced Acute Brain Injury and Functional Alterations in Mice
Yingyu Lu, Wanlu Zhou, Qinghua Cui, Chunmei Cui
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(15): 12244. CrossRef - AM1638, a GPR40-Full Agonist, Inhibited Palmitate- Induced ROS Production and Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress, Enhancing HUVEC Viability in an NRF2-Dependent Manner
Hwan-Jin Hwang, Joo Won Kim, SukHwan Yun, Min Jeong Park, Eyun Song, Sooyeon Jang, Ahreum Jang, Kyung Mook Choi, Sei Hyun Baik, Hye Jin Yoo
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(6): 760. CrossRef - Learn from failures and stay hopeful to GPR40, a GPCR target with robust efficacy, for therapy of metabolic disorders
Hong-Ping Guan, Yusheng Xiong
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Synthetic GPR40/FFAR1 agonists: An exhaustive survey on the most recent chemical classes and their structure-activity relationships
- Technology/Device
- Do-It-Yourself Open Artificial Pancreas System in Children and Adolescents with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus: Real-World Data
- Min Sun Choi, Seunghyun Lee, Jiwon Kim, Gyuri Kim, Sung Min Park, Jae Hyeon Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(1):154-159. Published online November 23, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0011

- 5,305 View
- 192 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Few studies have been conducted among Asian children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) using do-it-yourself artificial pancreas system (DIY-APS). We evaluated real-world data of pediatric T1DM patients using DIY-APS. Data were obtained for 10 patients using a DIY-APS with algorithms. We collected sensor glucose and insulin delivery data from each participant for a period of 4 weeks. Average glycosylated hemoglobin was 6.2%±0.3%. The mean percentage of time that glucose level remained in the target range of 70 to 180 mg/dL was 82.4%±7.8%. Other parameters including time above range, time below range and mean glucose were also within the recommended level, similar to previous commercial and DIY-APS studies. However, despite meeting the target range, unadjusted gaps were still observed between the median basal setting and temporary basal insulin, which should be handled by healthcare providers.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Advances in Continuous Glucose Monitoring and Integrated Devices for Management of Diabetes with Insulin-Based Therapy: Improvement in Glycemic Control
Jee Hee Yoo, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(1): 27. CrossRef - Open-source automated insulin delivery systems (OS-AIDs) in a pediatric population with type 1 diabetes in a real-life setting: the AWeSoMe study group experience
Judith Nir, Marianna Rachmiel, Abigail Fraser, Yael Lebenthal, Avivit Brener, Orit Pinhas-Hamiel, Alon Haim, Eve Stern, Noa Levek, Tal Ben-Ari, Zohar Landau
Endocrine.2023; 81(2): 262. CrossRef - Efficacy and safety of Android artificial pancreas system use at home among adults with type 1 diabetes mellitus in China: protocol of a 26-week, free-living, randomised, open-label, two-arm, two-phase, crossover trial
Mengyun Lei, Beisi Lin, Ping Ling, Zhigu Liu, Daizhi Yang, Hongrong Deng, Xubin Yang, Jing Lv, Wen Xu, Jinhua Yan
BMJ Open.2023; 13(8): e073263. CrossRef - Barriers to Uptake of Open-Source Automated Insulin Delivery Systems: Analysis of Socioeconomic Factors and Perceived Challenges of Caregivers of Children and Adolescents With Type 1 Diabetes From the OPEN Survey
Antonia Huhndt, Yanbing Chen, Shane O’Donnell, Drew Cooper, Hanne Ballhausen, Katarzyna A. Gajewska, Timothée Froment, Mandy Wäldchen, Dana M. Lewis, Klemens Raile, Timothy C. Skinner, Katarina Braune
Frontiers in Clinical Diabetes and Healthcare.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Toward Personalized Hemoglobin A1c Estimation for Type 2 Diabetes
Namho Kim, Da Young Lee, Wonju Seo, Nan Hee Kim, Sung-Min Park
IEEE Sensors Journal.2022; 22(23): 23023. CrossRef
- Advances in Continuous Glucose Monitoring and Integrated Devices for Management of Diabetes with Insulin-Based Therapy: Improvement in Glycemic Control
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
- A Comparison of Predictive Performances between Old versus New Criteria in a Risk-Based Screening Strategy for Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
- Subeen Hong, Seung Mi Lee, Soo Heon Kwak, Byoung Jae Kim, Ja Nam Koo, Ig Hwan Oh, Sohee Oh, Sun Min Kim, Sue Shin, Won Kim, Sae Kyung Joo, Errol R. Norwitz, Souphaphone Louangsenlath, Chan-Wook Park, Jong Kwan Jun, Joong Shin Park
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(5):726-736. Published online April 13, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0126
- 6,621 View
- 123 Download
- 9 Web of Science
- 9 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
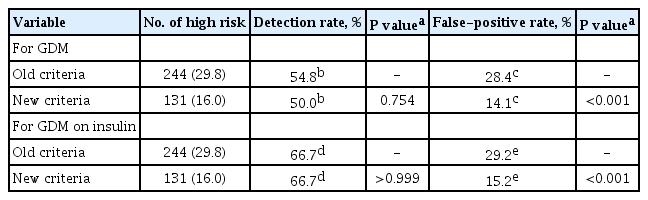
ePub Background The definition of the high-risk group for gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) defined by the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists was changed from the criteria composed of five historic/demographic factors (old criteria) to the criteria consisting of 11 factors (new criteria) in 2017. To compare the predictive performances between these two sets of criteria.
Methods This is a secondary analysis of a large prospective cohort study of non-diabetic Korean women with singleton pregnancies designed to examine the risk of GDM in women with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Maternal fasting blood was taken at 10 to 14 weeks of gestation and measured for glucose and lipid parameters. GDM was diagnosed by the two-step approach.
Results Among 820 women, 42 (5.1%) were diagnosed with GDM. Using the old criteria, 29.8% (
n =244) of women would have been identified as high risk versus 16.0% (n =131) using the new criteria. Of the 42 women who developed GDM, 45.2% (n =19) would have been mislabeled as not high risk by the old criteria versus 50.0% (n =21) using the new criteria (1-sensitivity, 45.2% vs. 50.0%,P >0.05). Among the 778 patients who did not develop GDM, 28.4% (n =221) would have been identified as high risk using the old criteria versus 14.1% (n =110) using the new criteria (1-specificity, 28.4% vs. 14.1%,P <0.001).Conclusion Compared with the old criteria, use of the new criteria would have decreased the number of patients identified as high risk and thus requiring early GDM screening by half (from 244 [29.8%] to 131 [16.0%]).
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Predicting the Risk of Insulin-Requiring Gestational Diabetes before Pregnancy: A Model Generated from a Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study in Korea
Seung-Hwan Lee, Jin Yu, Kyungdo Han, Seung Woo Lee, Sang Youn You, Hun-Sung Kim, Jae-Hyoung Cho, Kun-Ho Yoon, Mee Kyoung Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(1): 129. CrossRef - Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease and Subsequent Development of Adverse Pregnancy Outcomes
Seung Mi Lee, Young Mi Jung, Eun Saem Choi, Soo Heon Kwak, Ja Nam Koo, Ig Hwan Oh, Byoung Jae Kim, Sun Min Kim, Sang Youn Kim, Gyoung Min Kim, Sae Kyung Joo, Bo Kyung Koo, Sue Shin, Errol R. Norwitz, Chan-Wook Park, Jong Kwan Jun, Won Kim, Joong Shin Park
Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.2022; 20(11): 2542. CrossRef - Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and early prediction of gestational diabetes mellitus using machine learning methods
Seung Mi Lee, Suhyun Hwangbo, Errol R. Norwitz, Ja Nam Koo, Ig Hwan Oh, Eun Saem Choi, Young Mi Jung, Sun Min Kim, Byoung Jae Kim, Sang Youn Kim, Gyoung Min Kim, Won Kim, Sae Kyung Joo, Sue Shin, Chan-Wook Park, Taesung Park, Joong Shin Park
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2022; 28(1): 105. CrossRef - Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease-based risk prediction of adverse pregnancy outcomes: Ready for prime time?
Seung Mi Lee, Won Kim
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2022; 28(1): 47. CrossRef - Postprandial Free Fatty Acids at Mid-Pregnancy Increase the Risk of Large-for-Gestational-Age Newborns in Women with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
So-Yeon Kim, Young Shin Song, Soo-Kyung Kim, Yong-Wook Cho, Kyung-Soo Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(1): 140. CrossRef - Effect of Different Types of Diagnostic Criteria for Gestational Diabetes Mellitus on Adverse Neonatal Outcomes: A Systematic Review, Meta-Analysis, and Meta-Regression
Fahimeh Ramezani Tehrani, Marzieh Saei Ghare Naz, Razieh Bidhendi-Yarandi, Samira Behboudi-Gandevani
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(4): 605. CrossRef - Development of early prediction model for pregnancy-associated hypertension with graph-based semi-supervised learning
Seung Mi Lee, Yonghyun Nam, Eun Saem Choi, Young Mi Jung, Vivek Sriram, Jacob S. Leiby, Ja Nam Koo, Ig Hwan Oh, Byoung Jae Kim, Sun Min Kim, Sang Youn Kim, Gyoung Min Kim, Sae Kyung Joo, Sue Shin, Errol R. Norwitz, Chan-Wook Park, Jong Kwan Jun, Won Kim,
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The Clinical Characteristics of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus in Korea: A National Health Information Database Study
Kyung-Soo Kim, Sangmo Hong, Kyungdo Han, Cheol-Young Park
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(3): 628. CrossRef - The risk of pregnancy‐associated hypertension in women with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
Young Mi Jung, Seung Mi Lee, Subeen Hong, Ja Nam Koo, Ig Hwan Oh, Byoung Jae Kim, Sun Min Kim, Sang Youn Kim, Gyoung Min Kim, Sae Kyung Joo, Sue Shin, Errol R. Norwitz, Chan‐Wook Park, Jong Kwan Jun, Won Kim, Joong Shin Park
Liver International.2020; 40(10): 2417. CrossRef
- Predicting the Risk of Insulin-Requiring Gestational Diabetes before Pregnancy: A Model Generated from a Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study in Korea
- Basic Research
- Notch1 Has an Important Role in β-Cell Mass Determination and Development of Diabetes
- Young Sil Eom, A-Ryeong Gwon, Kyung Min Kwak, Jin-Young Youn, Heekyoung Park, Kwang-Won Kim, Byung-Joon Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(1):86-96. Published online February 26, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0160

- 6,334 View
- 185 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
Background Notch signaling pathway plays an important role in regulating pancreatic endocrine and exocrine cell fate during pancreas development. Notch signaling is also expressed in adult pancreas. There are few studies on the effect of Notch on adult pancreas. Here, we investigated the role of Notch in islet mass and glucose homeostasis in adult pancreas using Notch1 antisense transgenic (NAS).
Methods Western blot analysis was performed for the liver of 8-week-old male NAS mice. We also conducted an intraperitoneal glucose tolerance test (IPGTT) and intraperitoneal insulin tolerance test in 8-week-old male NAS mice and male C57BL/6 mice (control). Morphologic observation of pancreatic islet and β-cell was conducted in two groups. Insulin secretion capacity in islets was measured by glucose-stimulated insulin secretion (GSIS) and perifusion.
Results NAS mice showed higher glucose levels and lower insulin secretion in IPGTT than the control mice. There was no significant difference in insulin resistance. Total islet and β-cell masses were decreased in NAS mice. The number of large islets (≥250 µm) decreased while that of small islets (<250 µm) increased. Reduced insulin secretion was observed in GSIS and perifusion. Neurogenin3, neurogenic differentiation, and MAF bZIP transcription factor A levels increased in NAS mice.
Conclusion Our study provides that Notch1 inhibition decreased insulin secretion and decreased islet and β-cell masses. It is thought that Notch1 inhibition suppresses islet proliferation and induces differentiation of small islets. In conclusion, Notch signaling pathway may play an important role in β-cell mass determination and diabetes.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- N6-methylation of RNA-bound adenosine regulator HNRNPC promotes vascular endothelial dysfunction in type 2 diabetes mellitus by activating the PSEN1-mediated Notch pathway
Ying Cai, Tao Chen, Mingzhu Wang, Lihua Deng, Cui Li, Siqian Fu, Kangling Xie
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2023; 197: 110261. CrossRef - Single‐cell RNA sequencing: Inhibited Notch2 signalling underlying the increased lens fibre cells differentiation in high myopia
Yunqian Yao, Ling Wei, Zhenhua Chen, Hao Li, Jiao Qi, Qingfeng Wu, Xingtao Zhou, Yi Lu, Xiangjia Zhu
Cell Proliferation.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Micro ribonucleic acid‐363 regulates the phosphatidylinositol 3‐kinase/threonine protein kinase axis by targeting NOTCH1 and forkhead box C2, leading to hepatic glucose and lipids metabolism disorder in type 2 diabetes mellitus
Yu‐Huan Peng, Ping Wang, Xiao‐Qun He, Ming‐Zhao Hong, Feng Liu
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2022; 13(2): 236. CrossRef - Soluble T-cadherin promotes pancreatic β-cell proliferation by upregulating Notch signaling
Tomonori Okita, Shunbun Kita, Shiro Fukuda, Keita Fukuoka, Emi Kawada-Horitani, Masahito Iioka, Yuto Nakamura, Yuya Fujishima, Hitoshi Nishizawa, Dan Kawamori, Taka-aki Matsuoka, Maeda Norikazu, Iichiro Shimomura
iScience.2022; 25(11): 105404. CrossRef - Comparison of islet isolation result and clinical applicability according to GMP‐grade collagenase enzyme blend in adult porcine islet isolation and culture
Kyungmin Kwak, Jae‐kyung Park, Joohyun Shim, Nayoung Ko, Hyoung‐Joo Kim, Yongjin Lee, Jun‐Hyeong Kim, Michael Alexander, Jonathan R. T. Lakey, Hyunil Kim, Kimyung Choi
Xenotransplantation.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Genome-Wide Meta-analysis Identifies Genetic Variants Associated With Glycemic Response to Sulfonylureas
Adem Y. Dawed, Sook Wah Yee, Kaixin Zhou, Nienke van Leeuwen, Yanfei Zhang, Moneeza K. Siddiqui, Amy Etheridge, Federico Innocenti, Fei Xu, Josephine H. Li, Joline W. Beulens, Amber A. van der Heijden, Roderick C. Slieker, Yu-Chuan Chang, Josep M. Mercade
Diabetes Care.2021; 44(12): 2673. CrossRef
- N6-methylation of RNA-bound adenosine regulator HNRNPC promotes vascular endothelial dysfunction in type 2 diabetes mellitus by activating the PSEN1-mediated Notch pathway
- Complications
- Diabetes and Cancer: Cancer Should Be Screened in Routine Diabetes Assessment
- Sunghwan Suh, Kwang-Won Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2019;43(6):733-743. Published online December 23, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0177
- 8,649 View
- 262 Download
- 83 Web of Science
- 87 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Cancer incidence appears to be increased in both type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus (DM). DM represents a risk factor for cancer, particularly hepatocellular, hepatobiliary, pancreas, breast, ovarian, endometrial, and gastrointestinal cancers. In addition, there is evidence showing that DM is associated with increased cancer mortality. Common risk factors such as age, obesity, physical inactivity and smoking may contribute to increased cancer risk in patients with DM. Although the mechanistic process that may link diabetes to cancer is not completely understood yet, biological mechanisms linking DM and cancer are hyperglycemia, hyperinsulinemia, increased bioactivity of insulin-like growth factor 1, oxidative stress, dysregulations of sex hormones, and chronic inflammation. However, cancer screening rate is significantly lower in people with DM than that in people without diabetes. Evidence from previous studies suggests that some medications used to treat DM are associated with either increased or reduced risk of cancer. However, there is no strong evidence supporting the association between the use of anti-hyperglycemic medication and specific cancer. In conclusion, all patients with DM should be undergo recommended age- and sex appropriate cancer screenings to promote primary prevention and early detection. Furthermore, cancer should be screened in routine diabetes assessment.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- 4. Comprehensive Medical Evaluation and Assessment of Comorbidities: Standards of Care in Diabetes—2024
Nuha A. ElSayed, Grazia Aleppo, Raveendhara R. Bannuru, Dennis Bruemmer, Billy S. Collins, Kenneth Cusi, Laya Ekhlaspour, Talya K. Fleming, Marisa E. Hilliard, Eric L. Johnson, Kamlesh Khunti, Ildiko Lingvay, Glenn Matfin, Rozalina G. McCoy, Nicola Napoli
Diabetes Care.2024; 47(Supplement): S52. CrossRef - Editorial: The relationship between diabetes and cancers and its underlying mechanisms, volume II
Qiang Huo, Shuo Wang, Ying Hou, Reginald M. Gorczynski, Yining Shen, Bin Wang, Hanyi Ge, Tao Li
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors associated with gastric and duodenal neuroendocrine tumors: A multicenter case-control study
Kwangwoo Nam, Su Youn Nam, Jun Chul Park, Young Sin Cho, Hyuk Soon Choi, Kyoungwon Jung, Seon-Young Park, Joon Hyun Cho, Hyonho Chun
Digestive and Liver Disease.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Exploring Perspectives on Cancer Screening in People Aged 30-70: A Comparative Study of Those With and Without Type 2 Diabetes
Yunus GÜR, Egemen TURAL, Akın DAYAN
Konuralp Tıp Dergisi.2024; 16(1): 26. CrossRef - Prognostic significance of glucose‐lipid metabolic index in pancreatic cancer patients with diabetes mellitus
Hailiang Wang, Shiye Ruan, Zelong Wu, Qian Yan, Yubin Chen, Jinwei Cui, Zhongyan Zhang, Shanzhou Huang, Baohua Hou, Chuanzhao Zhang
Cancer Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Preoperative glucose-to-lymphocyte ratio predicts survival in cancer
Le Liu, Bei-bei Zhang, Yuan-zhou Li, Wen-juan Huang, Ye Niu, Qing-chun Jia, Wen Wang, Jia-rui Yuan, Shi-di Miao, Rui-tao Wang, Guang-yu Wang
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Higher Prevalence of Cancer in Patients with Diabetic Foot Syndrome
Chiara Goretti, Alessandro Prete, Alex Brocchi, Elisabetta Iacopi, Letizia Pieruzzi, Alberto Piaggesi
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2024; 13(5): 1448. CrossRef - Patterns and Trends in Mortality Associated With and Due to Diabetes Mellitus in a Transitioning Region With 3.17 Million People: Observational Study
Xiaopan Li, Ru Liu, Yichen Chen, Yan Han, Qizhe Wang, Yaxin Xu, Jing Zhou, Sunfang Jiang
JMIR Public Health and Surveillance.2023; 9: e43687. CrossRef - Diabetes and cancer: Optimising glycaemic control
Nalinie Joharatnam‐Hogan, Daniel L. Morganstein
Journal of Human Nutrition and Dietetics.2023; 36(2): 504. CrossRef - Need for improving immunization status and preventive care in diabetes mellitus patients
Teresa Gisinger, Alexandra Kautzky-Willer, Michael Leutner
Wiener klinische Wochenschrift.2023; 135(13-14): 336. CrossRef - Impact of cumulative hyperglycemic burden on the pancreatic cancer risk: A nationwide cohort study
Dong-Hoe Koo, Kyungdo Han, Cheol-Young Park
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2023; 195: 110208. CrossRef - Simultaneous Quantification of Serum Lipids and Their Association with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus-Positive Hepatocellular Cancer
Zhihong Yue, Lin Pei, Guangyan Meng, Aimin Zhang, Meng Li, Mei Jia, Hui Wang, Linlin Cao
Metabolites.2023; 13(1): 90. CrossRef - Modifiable risk factors for oral cavity cancer in non-smokers: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Margaret A. Heller, Sarah C. Nyirjesy, Robert Balsiger, Nicholas Talbot, Kyle K. VanKoevering, Catherine T. Haring, Matthew O. Old, Stephen Y. Kang, Nolan B. Seim
Oral Oncology.2023; 137: 106300. CrossRef - Hypertension, type 2 diabetes, obesity, and p53 mutations negatively correlate with metastatic colorectal cancer patients’ survival
Alessandro Ottaiano, Mariachiara Santorsola, Luisa Circelli, Francesco Perri, Marco Cascella, Francesco Sabbatino, Maurizio Capuozzo, Vincenza Granata, Silvia Zappavigna, Angela Lombardi, Marianna Scrima, Nadia Petrillo, Monica Ianniello, Marika Casillo,
Frontiers in Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The relationship between the CUN-BAE body fatness index and incident diabetes: a longitudinal retrospective study
Qing Peng, Zihao Feng, Zhuojian Cai, Dixing Liu, Jiana Zhong, Hejia Zhao, Xiuwei Zhang, Weikun Chen
Lipids in Health and Disease.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of four lipid-derived indicators with the risk of developing type 2 diabetes: a Chinese population-based cohort study
Linfeng He, Wenbin Zheng, Zeyu Li, Wen Kong, Tianshu Zeng
Lipids in Health and Disease.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Screening for Coronary Artery Disease in Cancer Survivors
Ragani Velusamy, Mark Nolan, Andrew Murphy, Paaladinesh Thavendiranathan, Thomas H. Marwick
JACC: CardioOncology.2023; 5(1): 22. CrossRef - Diabetes mellitus induces a novel inflammatory network involving cancer progression: Insights from bioinformatic analysis and in vitro validation
Yejun Tan, Jin Kang, Hongli Li, Aifang Zhong, Yaqiong Liu, Zheyu Zhang, Roujie Huang, Xin Cheng, Weijun Peng
Frontiers in Immunology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Increased Breast and Colorectal Cancer Risk in Type 2 Diabetes: Awareness Among Adults With and Without Diabetes and Information Provision on Diabetes Websites
Laura Ashley, Kathryn A Robb, Daryl B O’Connor, Rebecca Platt, Mollie Price, Olivia Robinson, Elizabeth Travis, Lorraine Lipscombe, Ramzi Ajjan, Rebecca Birch
Annals of Behavioral Medicine.2023; 57(5): 386. CrossRef - Primary peritoneal serous psammocarcinoma, rare variant: A case report
Srujan Kancharla, Anne Alaniz, Pulin Kothari, Stacy Norton
Gynecologic Oncology Reports.2023; 47: 101176. CrossRef - Association between the Finnish Diabetes Risk Score and cancer in middle-aged and older adults: Involvement of inflammation
Yu Peng, Peng Wang, Jianxiao Gong, Fubin Liu, Yating Qiao, Changyu Si, Xixuan Wang, Huijun Zhou, Fangfang Song
Metabolism.2023; 144: 155586. CrossRef - Interlinking of diabetes mellitus and cancer: An overview
Iftikhar Ahmad, Mohd Suhail, Ausaf Ahmad, Mahmoud Alhosin, Shams Tabrez
Cell Biochemistry and Function.2023; 41(5): 506. CrossRef - High glucose promotes the progression of colorectal cancer by activating the BMP4 signaling and inhibited by glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist
Bingwei Ma, Xingchun Wang, Hui Ren, Yingying Li, Haijiao Zhang, Muqing Yang, Jiyu Li
BMC Cancer.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Diabetes mellitus and the female reproductive system tumors
K. I. Sharafutdinova, V. S. Shlyapina, A. I. Baeva, A. A. Timurshin, I. E. Sabanaeva, A. G. Nakieva, M. F. Kalashnikova, M. N. Khabibov
Problems of Endocrinology.2023; 69(3): 103. CrossRef - Global estimates of rehabilitation needs and disease burden in tracheal, bronchus, and lung cancer from 1990 to 2019 and projections to 2045 based on the global burden of disease study 2019
Xigui Lai, Conghui Li, Yao Yang, Mingyuan Niu, Yujie Yang, Shanshan Gu, Weiqian Hou, Lili Chen, Yi Zhu
Frontiers in Oncology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Social and racial inequalities in diabetes and cancer in the United States
Nour Massouh, Ayad A. Jaffa, Hani Tamim, Miran A. Jaffa
Frontiers in Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Lactate in exhaled breath condensate and its correlation to cancer: challenges, promises and a call for data
Veronika Ruzsányi, Miklós Péter Kalapos
Journal of Breath Research.2023; 17(4): 044001. CrossRef - The impact of diabetes status on total and site-specific cancer risk in the elderly population: A nationwide cohort study
Kyuho Kim, Bongseong Kim, Hyunho Kim, Hyung Soon Park, Yu-Bae Ahn, Seung-Hyun Ko, Kyungdo Han, Jae-Seung Yun
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2023; 203: 110866. CrossRef - Team-Based Approach to Reduce Malignancies in People with Diabetes and Obesity
Ziyue Zhu, Samuel Yeung Shan Wong, Joseph Jao Yiu Sung, Thomas Yuen Tung Lam
Current Diabetes Reports.2023; 23(10): 253. CrossRef - PECAM-1 drives β-catenin-mediated EndMT via internalization in colon cancer with diabetes mellitus
Qing Wu, Xingxing Du, Jianing Cheng, Xiuying Qi, Huan Liu, Xiaohong Lv, Xieyang Gong, Changxin Shao, Muhong Wang, Luxiao Yue, Xin Yang, Shiyu Li, Yafang Zhang, Xuemei Li, Huike Yang
Cell Communication and Signaling.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Saxagliptin, a selective dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor, alleviates somatic cell aneugenicity and clastogenicity in diabetic mice
Sabry M. Attia, Sheikh F. Ahmad, Ahmed Nadeem, Mohamed S.M. Attia, Mushtaq A. Ansari, Abdelkader E. Ashour, Norah A. Albekairi, Mohammed A. Al-Hamamah, Ali A. Alshamrani, Saleh A. Bakheet
Mutation Research/Genetic Toxicology and Environmental Mutagenesis.2023; 892: 503707. CrossRef - Analysis of differential membrane proteins related to matrix stiffness-mediated metformin resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma cells
Xiangyu Gao, Jiali Qian, Yang Zhang, Heming Wang, Jiefeng Cui, Yehong Yang
Proteome Science.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Associations of heart failure to prevalence of haematologic- and solid malignancies in southern Sweden: A cross-sectional study
Mia Scholten, Anders Halling, Kathleen Bennett
PLOS ONE.2023; 18(10): e0292853. CrossRef - The interplay between antidiabetic medications and cancer risk
Duaa Durrani, Muhammad Hassan, Aimen Zulfikar
International Journal of Scientific Reports.2023; 9(11): 384. CrossRef - Causal association between inflammatory bowel disease and 32 site-specific extracolonic cancers: a Mendelian randomization study
Hui Gao, Shuhao Zheng, Xin Yuan, Jiarong Xie, Lei Xu
BMC Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between diabetes at different diagnostic ages and risk of cancer incidence and mortality: a cohort study
Yu Peng, Fubin Liu, Peng Wang, Yating Qiao, Changyu Si, Xixuan Wang, Jianxiao Gong, Huijun Zhou, Fengju Song, Fangfang Song
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The Characteristics and Risk of Mortality in the Elderly Korean Population
Sunghwan Suh
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(5): 522. CrossRef - Clinical potentials of metformin in cancer therapy
Nidhi Sharma, Richa Dhingra
Journal of Diabetology.2023; 14(4): 186. CrossRef - High Glucose Induced Upregulation of Cyclin a Associating with a Short Survival of Patients with Cholangiocarcinoma: A Potential Target for Treatment of Patients with Diabetes Mellitus
Charupong Saengboonmee, Marutpong Detarya, Sakkarn Sangkhamanon, Kanlayanee Sawanyawisuth, Wunchana Seubwai, Sopit Wongkham
Nutrition and Cancer.2022; 74(5): 1734. CrossRef - Prevalence of diabetes mellitus among 80,193 gastrointestinal cancer patients in five European and three Asian countries
Christoph Roderburg, Sven H. Loosen, Laura Hoyer, Tom Luedde, Karel Kostev
Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology.2022; 148(5): 1057. CrossRef - Metformin and survival: Is there benefit in a cohort limited to diabetic women with endometrial, breast, or ovarian cancer?
Lara S. Lemon, Brian Orr, Francesmary Modugno, Ronald J. Buckanovich, Lan Coffman, Robert P. Edwards, Sarah Taylor
Gynecologic Oncology.2022; 165(1): 60. CrossRef - The Relationship Between Diabetes Mellitus and Cancers and Its Underlying Mechanisms
Bing Zhu, Shen Qu
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The impact of diabetes mellitus on levels of sex hormones and their receptors in tumor tissues in female rats with Guerin’s carcinoma
E. M. Frantsiyants, V. A. Bandovkina, I. V. Kaplieva, E. I. Surikova, Yu. A. Pogorelova, N. D. Cheryarina, I. M. Kotieva, M. I. Morozova, A. I. Shikhlyarova
Research and Practical Medicine Journal.2022; 9(1): 23. CrossRef - Synergistic association between underweight and type 2 diabetes on the development of laryngeal cancer: a national population-based retrospective cohort study
Oh. Hyeong Lee, Yong-Moon Park, Seung-Hyun Ko, Kyuna Lee, Yeonji Kim, Kyungdo Han, Jung-Hae Cho
BMC Cancer.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Survival Risk Analysis of Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients with Pre-Existing Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Single-Center Retrospective Cohort Study
Jing Ding, Xudong Li, Jun Ge, Yuanqian Gong, Ya Zhou, Juan Xiao, Qin Yang, Jing Chen, Mian Mao
Cancer Management and Research.2022; Volume 14: 1313. CrossRef - The High Prevalence of Short-Term Elevation of Tumor Markers Due to Hyperglycemia in Diabetic Patients
Xi-yu Liu
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy.2022; Volume 15: 1113. CrossRef - Stationäre Patienten mit der Nebendiagnose Diabetes mellitus: klinische Relevanz
Christian Jenssen, Cristine Pietsch
Die Diabetologie.2022; 18(4): 379. CrossRef - Utility of Non-High-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol to High-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Ratio in Evaluating Incident Diabetes Risk
Guotai Sheng, Dingyang Liu, Maobin Kuang, Yanjia Zhong, Shuhua Zhang, Yang Zou
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy.2022; Volume 15: 1677. CrossRef - The Association of Dietary Fiber Intake in Three Meals with All-Cause and Disease-Specific Mortality among Adults: The U.S. National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 2003–2014
Jiayue Qi, Jian Gao, Yuntao Zhang, Wanying Hou, Tianshu Han, Changhao Sun
Nutrients.2022; 14(12): 2521. CrossRef - A Serum Metabolite Classifier for the Early Detection of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus-Positive Hepatocellular Cancer
Lin-Lin Cao, Yi Han, Lin Pei, Zhi-Hong Yue, Bo-Yu Liu, Jing-Wen Cui, Mei Jia, Hui Wang
Metabolites.2022; 12(7): 610. CrossRef - Extra-Glycemic Effects of Anti-Diabetic Medications: Two Birds with One Stone?
Eun-Jung Rhee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(3): 415. CrossRef - Improvement in Age at Mortality and Changes in Causes of Death in the Population with Diabetes: An Analysis of Data from the Korean National Health Insurance and Statistical Information Service, 2006 to 2018
Eugene Han, Sun Ok Song, Hye Soon Kim, Kang Ju Son, Sun Ha Jee, Bong-Soo Cha, Byung-Wan Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(3): 466. CrossRef - Novel insights into the pathogenic impact of diabetes on the gastrointestinal tract
Piero Portincasa, Leonilde Bonfrate, David Q.‐H. Wang, Gema Frühbeck, Gabriella Garruti, Agostino Di Ciaula
European Journal of Clinical Investigation.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Editorial: The relationship between diabetes and cancers and its underlying mechanisms
Qiang Huo, Jing Wang, Nannan Zhang, Long Xie, Heshan Yu, Tao Li
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Oxidatively Damaged Nucleic Acid: Linking Diabetes and Cancer
Xiujuan Hong, Yiqiu Hu, Zhijun Yuan, Zhihao Fang, Xiaoxiao Zhang, Ying Yuan, Cheng Guo
Antioxidants & Redox Signaling.2022; 37(16-18): 1153. CrossRef - Diabetes mellitus and endometrial carcinoma: Risk factors and etiological links
Ya Wang, Xinling Zeng, Jie Tan, Yi Xu, Cunjian Yi
Medicine.2022; 101(34): e30299. CrossRef - The Good, the Bad and the New about Uric Acid in Cancer
Simone Allegrini, Mercedes Garcia-Gil, Rossana Pesi, Marcella Camici, Maria Grazia Tozzi
Cancers.2022; 14(19): 4959. CrossRef - Family cancer history and smoking habit associated with sarcoma in a Japanese population study
Yoshihiro Araki, Norio Yamamoto, Yoshikazu Tanzawa, Takahiro Higashi, Aya Kuchiba, Katsuhiro Hayashi, Akihiko Takeuchi, Shinji Miwa, Kentaro Igarashi, Makoto Endo, Eisuke Kobayashi, Hiroyuki Tsuchiya, Akira Kawai
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Decreased IGF-1 level is associated with restrained amino acid metabolism in NSCLC with diabetes mellitus
Hehe Lv, Fan Zhang, Can Liang, Xuekui Liu, Yamei Ma, Jiayi Li, Yan Ye, Shanwen Si, Yaran Liu, Hao Heng, Houfa Geng
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Acute Pancreatitis Increases the Risk of Gastrointestinal Cancer in Type 2 Diabetic Patients: A Korean Nationwide Cohort Study
Jin Ho Choi, Woo Hyun Paik, Dong Kee Jang, Min Kyu Kim, Ji Kon Ryu, Yong-Tae Kim, Kyungdo Han, Sang Hyub Lee
Cancers.2022; 14(22): 5696. CrossRef - Targets for the prevention of comorbidity of cardiovascular and cancer diseases
M. N. Mamedov, K. K. Badeinikova, A. K. Karimov
Russian Journal of Cardiology.2022; 27(11): 5235. CrossRef - Prevalence and potential risk factors of self-reported diabetes among elderly people in China: A national cross-sectional study of 224,142 adults
Xing Hu, Lingbing Meng, Zhimin Wei, Hongxuan Xu, Jianyi Li, Yingying Li, Na Jia, Hui Li, Xin Qi, Xuezhai Zeng, Qiuxia Zhang, Juan Li, Deping Liu
Frontiers in Public Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Urinary Exosomal Tissue TIMP and Angiopoietin-1 Are Preoperative Novel Biomarkers of Well-Differentiated Thyroid Cancer
Chih-Yuan Wang, Shyang-Rong Shih, Kuen-Yuan Chen, Pei-Jie Huang
Biomedicines.2022; 11(1): 24. CrossRef - Acquired and modifiable cardiovascular risk factors in patients treated for cancer
Gary S. Beasley, Jeffrey A. Towbin
Journal of Thrombosis and Thrombolysis.2021; 51(4): 846. CrossRef - Diabetes and Cancer: Metabolic Association, Therapeutic Challenges, and the Role of Natural Products
Wamidh H. Talib, Asma Ismail Mahmod, Sara Feras. Abuarab, Eliza Hasen, Amer A. Munaim, Shatha Khaled Haif, Amani Marwan Ayyash, Samar Khater, Intisar Hadi AL-Yasari, Lina T. Al Kury
Molecules.2021; 26(8): 2179. CrossRef - Epidemiological link between obesity, type 2 diabetes mellitus and cancer
Cornelius J Fernandez, Annu Susan George, Nikhila A Subrahmanyan, Joseph M Pappachan
World Journal of Methodology.2021; 11(3): 23. CrossRef - Evaluation of the Efficacy of the Hospital Glycemic Management System for Patients with Malignant Tumors and Hyperglycemia
Juan Jiang, Danlan Pu, Renzhi Hu, Mingyang Hu, Qinan Wu
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy.2021; Volume 14: 2717. CrossRef - Insulin-Like Growth Factor 1 (IGF-1) Signaling in Glucose Metabolism in Colorectal Cancer
Aldona Kasprzak
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2021; 22(12): 6434. CrossRef - TNBC: Potential Targeting of Multiple Receptors for a Therapeutic Breakthrough, Nanomedicine, and Immunotherapy
Desh Deepak Singh, Dharmendra Kumar Yadav
Biomedicines.2021; 9(8): 876. CrossRef - GLP-1 Receptor Agonists: Beyond Their Pancreatic Effects
Xin Zhao, Minghe Wang, Zhitong Wen, Zhihong Lu, Lijuan Cui, Chao Fu, Huan Xue, Yunfeng Liu, Yi Zhang
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - The Aneugenicity of Ketone Bodies in Colon Epithelial Cells Is Mediated by Microtubule Hyperacetylation and Is Blocked by Resveratrol
Haruka Sudo, Akira Kubo
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2021; 22(17): 9397. CrossRef - EFFECT OF DIABETES MELLITUS ON THE LEVEL OF GROWTH FACTORS IN GUERIN CARCINOMA IN RATS OF BOTH SEXES
E.M. Frantsiyants, V.A. Bandovkina, I.V. Kaplieva, E.I. Surikova, I.V. Neskubina, L.K. Trepitaki, N.D. Cheryarina, Yu.A. Pogorelova, L.A. Nemashkalova, A.I. Shikhlyarova, I.M. Kotieva, M.I. Morozova
Ulyanovsk Medico-biological Journal.2021; : 129. CrossRef - Clinical Significance of Screening Differential Metabolites in Ovarian Cancer Tissue and Ascites by LC/MS
Miao Liu, Yu Liu, Hua Feng, Yixin Jing, Shuang Zhao, Shujia Yang, Nan Zhang, Shi Jin, Yafei Li, Mingjiao Weng, Xinzhu Xue, Fuya Wang, Yongheng Yang, Xiaoming Jin, Dan Kong
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Diabetes mellitus and cancer: a system of insulin-like growth factors
E. M. Frantsiyants, E. I. Surikova, I. V. Kaplieva, V. A. Bandovkina, I. V. Neskubina, E. A. Sheiko, M. I. Morozova, I. M. Kotieva
Problems of Endocrinology.2021; 67(5): 34. CrossRef - Diabetes and Cancer: Risk, Challenges, Management and Outcomes
Rabia K. Shahid, Shahid Ahmed, Duc Le, Sunil Yadav
Cancers.2021; 13(22): 5735. CrossRef - Obesity, Diabetes, and Increased Cancer Progression
Dae-Seok Kim, Philipp E. Scherer
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(6): 799. CrossRef - Simple Serum Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma (PDAC) Protein Biomarkers—Is There Anything in Sight?
Monika Kapszewicz, Ewa Małecka-Wojciesko
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2021; 10(22): 5463. CrossRef - Chronic non-communicable diseases, risk factors, and quality of life in patients with malignancies of various localizations
M.N. Mamedov, V.I. Potievskaya, E.K. Saribekyan, O.V. Pikin, D.V. Sidorov, Z.M. Salimov, V.A. Kutsenko, O.M. Drapkina
Profilakticheskaya meditsina.2021; 24(11): 45. CrossRef - Survival after breast cancer in women with type 2 diabetes using antidiabetic medication and statins: a retrospective cohort study
Mayu Hosio, Elina Urpilainen, Ari Hautakoski, Mikko Marttila, Martti Arffman, Reijo Sund, Anne Ahtikoski, Ulla Puistola, Peeter Karihtala, Arja Jukkola, Esa Läärä
Acta Oncologica.2020; 59(9): 1110. CrossRef - Transcriptional Profiling and Biological Pathway(s) Analysis of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in a Pakistani Population
Zarish Noreen, Christopher A. Loffredo, Attya Bhatti, Jyothirmai J. Simhadri, Gail Nunlee-Bland, Thomas Nnanabu, Peter John, Jahangir S. Khan, Somiranjan Ghosh
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(16): 5866. CrossRef - Screening Strategy of Pancreatic Cancer in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus
Suguru Mizuno, Yousuke Nakai, Kazunaga Ishigaki, Kei Saito, Hiroki Oyama, Tsuyoshi Hamada, Yukari Suzuki, Akiyuki Inokuma, Sachiko Kanai, Kensaku Noguchi, Tatsuya Sato, Ryunosuke Hakuta, Tomotaka Saito, Naminatsu Takahara, Hirofumi Kogure, Hiroyuki Isayam
Diagnostics.2020; 10(8): 572. CrossRef - Changes in mortality rates and ratios in people with pharmacologically treated type 2 diabetes mellitus between 2001 and 2016 in Hungary
György Jermendy, Zoltán Kiss, György Rokszin, Ibolya Fábián, István Wittmann, Péter Kempler
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2020; 163: 108134. CrossRef Role of αVβ3 in Prostate Cancer: Metastasis Initiator and Important Therapeutic Target
Lin Tang, Meng Xu, Long Zhang, Lin Qu, Xiaoyan Liu
OncoTargets and Therapy.2020; Volume 13: 7411. CrossRef- Arterial stiffness is an independent predictor for risk of mortality in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: the REBOUND study
Jeong Mi Kim, Sang Soo Kim, In Joo Kim, Jong Ho Kim, Bo Hyun Kim, Mi Kyung Kim, Soon Hee Lee, Chang Won Lee, Min Chul Kim, Jun Hyeob Ahn, Jinmi Kim
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - An Overview of Cancer Prevention: Chemoprevention and Immunoprevention
Kyle J. Gu, Guojun Li
Journal of Cancer Prevention.2020; 25(3): 127. CrossRef - Type 2 diabetes mellitus facilitates endometrial hyperplasia progression by activating the proliferative function of mucin O-glycosylating enzyme GALNT2
Xueyan Zhou, Yinxue Xu, Di Yin, Feng Zhao, Zhixiang Hao, Ya’nan Zhong, Jingbo Zhang, Bei Zhang, Xiaoxing Yin
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2020; 131: 110764. CrossRef - Diabetes mellitus and the risk of ovarian cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort and case–control studies
Lihai Wang, Lei Zhong, Bin Xu, Min Chen, Hongxiao Huang
BMJ Open.2020; 10(12): e040137. CrossRef
- 4. Comprehensive Medical Evaluation and Assessment of Comorbidities: Standards of Care in Diabetes—2024
- Clinical Care/Education
- Impact of Socioeconomic Status on Health Behaviors, Metabolic Control, and Chronic Complications in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- So Hun Kim, Seung Youn Lee, Chei Won Kim, Young Ju Suh, Seongbin Hong, Seong Hee Ahn, Da Hae Seo, Moon-Suk Nam, Suk Chon, Jeong-Taek Woo, Sei Hyun Baik, Yongsoo Park, Kwan Woo Lee, Young Seol Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2018;42(5):380-393. Published online June 29, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2017.0102
- 4,837 View
- 67 Download
- 11 Web of Science
- 15 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader Background The aim of the study was to assess the impact of socioeconomic status (SES) on health behaviors, metabolic control, and chronic complications in people with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) from South Korea, a country with universal health insurance coverage and that has experienced rapid economic and social transition.
Methods A total of 3,294 Korean men and women with T2DM aged 30 to 65 years, participating in the Korean National Diabetes Program (KNDP) cohort who reported their SES and had baseline clinical evaluation were included in the current cross-sectional analysis. SES included the level of education and monthly household income.
Results Lower education level and lower income level were closely related, and both were associated with older age in men and women. Women and men with lower income and education level had higher carbohydrate and lower fat intake. After adjustment for possible confounding factors, higher education in men significantly lowered the odds of having uncontrolled hyperglycemia (glycosylated hemoglobin ≥7.5%) (odds ratio [OR], 0.63; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.43 to 0.91 for highest education;
P trend=0.048), while higher household income in men significantly lowered the odds of having diabetic retinopathy (OR, 0.59; 95% CI, 0.37 to 0.95 for highest income level;P trend=0.048). In women, lower income was associated with a higher stress level.Conclusion Men with lower SES had higher odds of having diabetic retinopathy and uncontrolled hyperglycemia, showing the need to improve care targeted to this population.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Scoping Review of Possible Solutions for Decreasing Socioeconomic Inequalities in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Laleh Gharacheh, Mostafa Amini-Rarani, Amin Torabipour, Saeed Karimi
International Journal of Preventive Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Socioeconomic status and the effect of prolonged pandemic confinement on anthropometric and glycaemic outcomes in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Chandana Wijeweera, Ummul Muhfaza, Reginald V. Lord, Peter Petocz, Juliana Chen, Veronica Preda
Primary Care Diabetes.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Income variability and incident cardiovascular disease in diabetes: a population-based cohort study
Yong-Moon Mark Park, Jong-Ha Baek, Hong Seok Lee, Tali Elfassy, Clare C Brown, Mario Schootman, Marie-Rachelle Narcisse, Seung-Hyun Ko, Pearl A McElfish, Michael R Thomsen, Benjamin C Amick, Seong-Su Lee, Kyungdo Han
European Heart Journal.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of diet quality with glycemia, insulinemia, and insulin resistance in families at high risk for type 2 diabetes mellitus in Europe: Feel4 Diabetes Study
Botsi E, Karatzi K, Mavrogianni C, Kaloyan Tsochev, Esther M González-Gil, Radó S, Kivelä J, Wikström K, Cardon G, Rurik I, Liatis S, Tsvetalina Tankova, Violeta Iotova, Luis A. Moreno, Makrillakis K, Manios Y, Tsigos C
Nutrition.2023; 105: 111805. CrossRef - Sustained Low Income, Income Changes, and Risk of All-Cause Mortality in Individuals With Type 2 Diabetes: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study
Hong Seok Lee, Jimin Clara Park, Inkwan Chung, Junxiu Liu, Seong-Su Lee, Kyungdo Han
Diabetes Care.2023; 46(1): 92. CrossRef - Association of birth weight with risk of diabetes mellitus in adolescence and early adulthood: analysis of the Indonesian Family Life Survey
Ratu Ayu Dewi Sartika, Fathimah Sulistyowati Sigit, Edy Purwanto, Norliyana Aris, Avliya Quratul Marjan, Wahyu Kurnia Yusrin Putra, Sutanto Priyo Hastono
Annals of Pediatric Endocrinology & Metabolism.2023; 28(4): 267. CrossRef - Effects of Diabetes Quality Assessment on Diabetes Management Behaviors Based on a Nationwide Survey
Chang Kyun Choi, Jungho Yang, Ji-An Jeong, Min-Ho Shin
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(23): 15781. CrossRef - FOLLOW-UP ADHERENCE IN PATIENTS WITH NONPROLIFERATIVE DIABETIC RETINOPATHY PRESENTING TO AN OPHTHALMIC EMERGENCY DEPARTMENT
Arjun Watane, Meghana Kalavar, Elizabeth A. Vanner, Kara Cavuoto, Jayanth Sridhar
Retina.2021; 41(6): 1293. CrossRef - Socioeconomic disparity in global vision loss burden due to diabetic retinopathy: an analysis on time trends from 1990 to 2017
Yi Shan, Yufeng Xu, Lingxia Ye, Xiling Lin, Yaoyao Chen, Qi Miao, Juan Ye
Endocrine.2021; 73(2): 316. CrossRef - Tip 2 Diyabetli Bireylerin Hastalık Yönetiminde Karşılaştıkları Engellerin Değerlendirilmesi
Şuheda ÜSTÜNDAĞ, Nuray DAYAPOĞLU
Adnan Menderes Üniversitesi Sağlık Bilimleri Fakültesi Dergisi.2021; 5(3): 514. CrossRef - Socioeconomic inequalities in type 2 diabetes in employed individuals, nonworking spouses and pensioners
Batoul Safieddine, Stefanie Sperlich, Johannes Beller, Karin Lange, Jelena Epping, Juliane Tetzlaff, Fabian Tetzlaff, Siegfried Geyer
SSM - Population Health.2020; 11: 100596. CrossRef - Thirteen-year trends in the prevalence of diabetes according to socioeconomic condition and cardiovascular risk factors in a Swiss population
Carlos de Mestral, Silvia Stringhini, Idris Guessous, François R Jornayvaz
BMJ Open Diabetes Research & Care.2020; 8(1): e001273. CrossRef - Dietary Habits and Dietary Antioxidant Intake Are Related to Socioeconomic Status in Polish Adults: A Nationwide Study
Małgorzata Elżbieta Zujko, Anna Waśkiewicz, Wojciech Drygas, Alicja Cicha-Mikołajczyk, Kinga Zujko, Danuta Szcześniewska, Krystyna Kozakiewicz, Anna Maria Witkowska
Nutrients.2020; 12(2): 518. CrossRef - Diabetes Fact Sheets in Korea, 2018: An Appraisal of Current Status
Bo-Yeon Kim, Jong Chul Won, Jae Hyuk Lee, Hun-Sung Kim, Jung Hwan Park, Kyoung Hwa Ha, Kyu Chang Won, Dae Jung Kim, Kyong Soo Park
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2019; 43(4): 487. CrossRef - Gender in Endocrine Diseases: Role of Sex Gonadal Hormones
R. Lauretta, M. Sansone, A. Sansone, F. Romanelli, M. Appetecchia
International Journal of Endocrinology.2018; 2018: 1. CrossRef
- A Scoping Review of Possible Solutions for Decreasing Socioeconomic Inequalities in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Others
- Generation of Insulin-Expressing Cells in Mouse Small Intestine by Pdx1, MafA, and BETA2/NeuroD
- So-Hyun Lee, Marie Rhee, Ji-Won Kim, Kun-Ho Yoon
- Diabetes Metab J. 2017;41(5):405-416. Published online September 5, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2017.41.5.405
- 5,109 View
- 64 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader Background To develop surrogate insulin-producing cells for diabetes therapy, adult stem cells have been identified in various tissues and studied for their conversion into β-cells. Pancreatic progenitor cells are derived from the endodermal epithelium and formed in a manner similar to gut progenitor cells. Here, we generated insulin-producing cells from the intestinal epithelial cells that induced many of the specific pancreatic transcription factors using adenoviral vectors carrying three genes: PMB (pancreatic and duodenal homeobox 1 [Pdx1], V-maf musculoaponeurotic fibrosarcoma oncogene homolog A [MafA], and BETA2/NeuroD).
Methods By direct injection into the intestine through the cranial mesenteric artery, adenoviruses (Ad) were successfully delivered to the entire intestine. After virus injection, we could confirm that the small intestine of the mouse was appropriately infected with the Ad-Pdx1 and triple Ad-PMB.
Results Four weeks after the injection, insulin mRNA was expressed in the small intestine, and the insulin gene expression was induced in Ad-Pdx1 and Ad-PMB compared to control Ad-green fluorescent protein. In addition, the conversion of intestinal cells into insulin-expressing cells was detected in parts of the crypts and villi located in the small intestine.
Conclusion These data indicated that PMB facilitate the differentiation of mouse intestinal cells into insulin-expressing cells. In conclusion, the small intestine is an accessible and abundant source of surrogate insulin-producing cells.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Harnessing gut cells for functional insulin production: Strategies and challenges
Kelvin Baafi, John C. March
Biotechnology Notes.2023; 4: 7. CrossRef - Differential Morphological Diagnosis of Various Forms of Congenital Hyperinsulinism in Children
Lubov Borisovna Mitrofanova, Anastasia Arkadyevna Perminova, Daria Viktorovna Ryzhkova, Anna Andreyevna Sukhotskaya, Vladimir Gireyevich Bairov, Irina Leorovna Nikitina
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Generation of iPSC-derived insulin-producing cells from patients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes compared with healthy control
Min Jung Kim, Eun Young Lee, Young-Hye You, Hae Kyung Yang, Kun-Ho Yoon, Ji-Won Kim
Stem Cell Research.2020; 48: 101958. CrossRef - ERK Regulates NeuroD1-mediated Neurite Outgrowth via Proteasomal Degradation
Tae-young Lee, In-Su Cho, Narayan Bashyal, Francisco J Naya, Ming-Jer Tsai, Jeong Seon Yoon, Jung-Mi Choi, Chang-Hwan Park, Sung-Soo Kim, Haeyoung Suh-Kim
Experimental Neurobiology.2020; 29(3): 189. CrossRef - Generation of a PDX1–EGFP reporter human induced pluripotent stem cell line, KSCBi005-A-3, using the CRISPR/Cas9 system
Youngsun Lee, Hye Young Choi, Ara Kwon, Hyeyeon Park, Mi-Hyun Park, Ji-Won Kim, Min Jung Kim, Yong-Ou Kim, Sungwook Kwak, Soo Kyung Koo
Stem Cell Research.2019; 41: 101632. CrossRef
- Harnessing gut cells for functional insulin production: Strategies and challenges
- Intensive Individualized Reinforcement Education Is Important for the Prevention of Hypoglycemia in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
- Yun-Mi Yong, Kyung-Mi Shin, Kang-Min Lee, Jae-Young Cho, Sun-Hye Ko, Min-Hyang Yoon, Tae-Won Kim, Jong-Hyun Jeong, Yong-Moon Park, Seung-Hyun Ko, Yu-Bae Ahn
- Diabetes Metab J. 2015;39(2):154-163. Published online March 10, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2015.39.2.154
- 3,954 View
- 40 Download
- 17 Web of Science
- 20 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader Background We investigated whether an intensive individualized reinforcement education program could influence the prevention of hypoglycemic events in patients with type 2 diabetes.
Methods From March 2013 to September 2013, patients aged 35 to 75 years with type 2 diabetes who had not previously participated in diabetes education, and treated with insulin or a sulfonylurea-containing regimen were included in the study. After structured group education, the patients assigned to the intensive individualized education group (IT) were requested to visit for reinforcement. All subjects in the IT were encouraged to self-manage dose adjustments. Participants in both groups (control group [CG, group education only;
n =22] and IT [n =24]) attended follow-up visits at 2, 8, 12, and 24 weeks. At each visit, all patients were asked whether they had experienced hypoglycemia.Results The total study population consisted of 20 men (43.5%; mean age and diabetic duration of 55.9±11.0 and 5.1±7.3 years, respectively). At 24 weeks, there were no significant differences in hemoglobin A1c values between the CG and IT. The total number of hypoglycemic events per patient was 5.26±6.5 in the CG and 2.58±2.3 times in the IT (
P =0.004). Adherence to lifestyle modification including frequency of exercise, self-monitoring of blood glucose, or dietary habit was not significantly different between the groups. However, adherence to hypoglycemia management, especially the dose adjustment of medication, was significantly higher in the IT compared with the CG.Conclusion Compared with the structured group education, additional IT resulted in additional benefits in terms of avoidance of hypoglycemia and treating hypoglycemia in patients with type 2 diabetes.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effectiveness of the SUGAR intervention on hypoglycaemia in elderly patients with type 2 diabetes: A pragmatic randomised controlled trial
Huda Y. Almomani, Carlos Rodriguez Pascual, Paul Grassby, Keivan Ahmadi
Research in Social and Administrative Pharmacy.2023; 19(2): 322. CrossRef - A Cross-Sectional study on risk factors for severe hypoglycemia among Insulin-Treated elderly type 2 diabetes Mellitus (T2DM) patients in Singapore
Michelle Shi Min Ko, Wai Kit Lee, Li Chang Ang, Su-Yen Goh, Yong Mong Bee, Ming Ming Teh
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2022; 185: 109236. CrossRef - Management Status of Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus at General Hospitals in Korea: A 5-Year Follow-Up Study
Jin Hee Jung, Jung Hwa Lee, Hyang Mi Jang, Young Na, Hee Sun Choi, Yeon Hee Lee, Yang Gyo Kang, Na Rae Kim, Jeong Rim Lee, Bok Rye Song, Kang Hee Sim
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2022; 23(1): 64. CrossRef - Anti-hyperglycemic Medication Compliance: A Quality Assurance Project
Rayan Mamoon, Md Y Mamoon, Debbie Hermanstyne, Issac Sachmechi
Cureus.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Randomised controlled trial of pharmacist-led patient counselling in controlling hypoglycaemic attacks in older adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus (ROSE-ADAM): A study protocol of the SUGAR intervention
Huda Y. Almomani, Carlos Rodriguez Pascual, Sayer I. Al-Azzam, Keivan Ahmadi
Research in Social and Administrative Pharmacy.2021; 17(5): 885. CrossRef - Severe hypoglycemia as a preventable risk factor for cardiovascular disease in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Soo-Yeon Choi, Seung-Hyun Ko
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2021; 36(2): 263. CrossRef - Type 2 diabetes patients’ views on prevention of hypoglycaemia – a mixed methods study investigating self-management issues and self-identified causes of hypoglycaemia
Stijn Crutzen, Tessa van den Born-Bondt, Petra Denig, Katja Taxis
BMC Family Practice.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Cross‐sectional analysis of emergency hypoglycaemia and outcome predictors among people with diabetes in an urban population
Chukwuma Uduku, Valentina Pendolino, Ian Godsland, Nick Oliver, Monika Reddy, Rachael T. Fothergill
Diabetic Medicine.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Short-term efficacy of high intensity group and individual education in patients with type 2 diabetes: a randomized single-center trial
R. Reale, A. Tumminia, L. Romeo, N. La Spina, R. Baratta, G. Padova, L. Tomaselli, L. Frittitta
Journal of Endocrinological Investigation.2019; 42(4): 403. CrossRef - The role of structured education in the management of hypoglycaemia
Ahmed Iqbal, Simon R. Heller
Diabetologia.2018; 61(4): 751. CrossRef - Association of diabetes therapy-related quality of life and physical activity levels in patients with type 2 diabetes receiving medication therapy: the Diabetes Distress and Care Registry at Tenri (DDCRT 17)
Yasuaki Hayashino, Satoru Tsujii, Hitoshi Ishii
Acta Diabetologica.2018; 55(2): 165. CrossRef - Insulin Therapy for Adult Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Position Statement of the Korean Diabetes Association, 2017
Byung-Wan Lee, Jin Hwa Kim, Seung-Hyun Ko, Kyu-Yeon Hur, Nan-Hee Kim, Sang Youl Rhee, Hyun Jin Kim, Min Kyong Moon, Seok-O Park, Kyung Mook Choi
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2017; 41(5): 367. CrossRef - Antihyperglycemic Agent Therapy for Adult Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus 2017: A Position Statement of the Korean Diabetes Association
Seung-Hyun Ko, Kyu-Yeon Hur, Sang Youl Rhee, Nan-Hee Kim, Min Kyong Moon, Seok-O Park, Byung-Wan Lee, Hyun Jin Kim, Kyung Mook Choi, Jin Hwa Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2017; 41(5): 337. CrossRef - Insulin therapy for adult patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a position statement of the Korean Diabetes Association, 2017
Byung-Wan Lee, Jin Hwa Kim, Seung-Hyun Ko, Kyu Yeon Hur, Nan-Hee Kim, Sang Youl Rhee, Hyun Jin Kim, Min Kyong Moon, Seok-O Park, Kyung Mook Choi
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2017; 32(6): 967. CrossRef - Physician-Directed Diabetes Education without a Medication Change and Associated Patient Outcomes
Hun-Sung Kim, Hyunah Kim, Hae-Kyung Yang, Eun Young Lee, Yoo Jin Jeong, Tong Min Kim, So Jung Yang, Seo Yeon Baik, Seung-Hwan Lee, Jae Hyoung Cho, In Young Choi, Hyeon Woo Yim, Bong-Yun Cha
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2017; 41(3): 187. CrossRef - Antihyperglycemic agent therapy for adult patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus 2017: a position statement of the Korean Diabetes Association
Seung-Hyun Ko, Kyu-Yeon Hur, Sang Youl Rhee, Nan-Hee Kim, Min Kyong Moon, Seok-O Park, Byung-Wan Lee, Hyun Jin Kim, Kyung Mook Choi, Jin Hwa Kim
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2017; 32(6): 947. CrossRef - Hypoglycemia and Health Costs
Yong-ho Lee, Gyuri Kim, Eun Seok Kang
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2016; 17(1): 11. CrossRef - Association between estimated blood glucose levels and glycated hemoglobin levels
Seon-Ah Cha, Seung-Hyun Ko
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2016; 31(3): 457. CrossRef - Characteristics of Hypoglycemia Pateints Visiting the Emergency Department of a University Hospital
Sang-Hyeon Choi, Deok-Ki Youn, Moon-Gi Choi, Ohk-Hyun Ryu
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2016; 17(3): 202. CrossRef - Experiences of Diabetes Education among Educators of Diabetes : a content analysis approach
Soo Jin Kang, Soo Jung Chang
Journal of Korean Public Health Nursing.2016; 30(2): 221. CrossRef
- Effectiveness of the SUGAR intervention on hypoglycaemia in elderly patients with type 2 diabetes: A pragmatic randomised controlled trial
- Effectiveness of 3-Day Continuous Glucose Monitoring for Improving Glucose Control in Type 2 Diabetic Patients in Clinical Practice
- Soo Kyoung Kim, Hye Jeong Kim, Taehun Kim, Kyu Yeon Hur, Sun Wook Kim, Moon-Kyu Lee, Yong-Ki Min, Kwang-Won Kim, Jae Hoon Chung, Jae Hyeon Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2014;38(6):449-455. Published online December 15, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2014.38.6.449
- 4,873 View
- 38 Download
- 16 Web of Science
- 16 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background The aim of this study was to investigate whether adjusting diabetic treatment regimens according to the information obtained from a continuous glucose monitoring system (CGMS) might lead to improved glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes.
Methods We reviewed the medical charts of 172 patients who used the CGMS for 1 year starting in December 2008 and the records of 1,500 patients who visited their regular outpatient clinics during December 2008. Of these patients, a total of 65 CGMS patients and 301 regular outpatients (control group) were enrolled in the study after propensity score matching. There were no differences in baseline glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c), age, and duration of diabetes between the CGMS and the control groups after propensity score matching. The changes in the HbA1c levels from baseline to 6 months were calculated.
Results The CGMS group showed a significant improvement in the HbA1c level compared to the control group at 3 months (7.9%±1.6% vs. 7.4%±1.2%,
P =0.001) and at 6 months (7.4%±1.2% vs. 7.9%±1.6%,P =0.010). There were significant differences in the treatment modality changes between the CGMS group and the control group.Conclusion Using a 3-day CGMS was advantageous for improving glucose control in patients with type 2 diabetes and may help these patients to optimize glycemic control in clinical practice.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Biological and Clinical Impacts of Glucose Metabolism in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma
Zhao Liu, Hiromitsu Hayashi, Kazuki Matsumura, Norio Uemura, Yuta Shiraishi, Hiroki Sato, Hideo Baba
Cancers.2023; 15(2): 498. CrossRef - Professional continuous glucose monitoring in patients with diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta‐analysis
Sergio Di Molfetta, Irene Caruso, Angelo Cignarelli, Annalisa Natalicchio, Sebastio Perrini, Luigi Laviola, Francesco Giorgino
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2023; 25(5): 1301. CrossRef - American Association of Clinical Endocrinology Clinical Practice Guideline: The Use of Advanced Technology in the Management of Persons With Diabetes Mellitus
George Grunberger, Jennifer Sherr, Myriam Allende, Thomas Blevins, Bruce Bode, Yehuda Handelsman, Richard Hellman, Rosemarie Lajara, Victor Lawrence Roberts, David Rodbard, Carla Stec, Jeff Unger
Endocrine Practice.2021; 27(6): 505. CrossRef - Lack of Acceptance of Digital Healthcare in the Medical Market: Addressing Old Problems Raised by Various Clinical Professionals and Developing Possible Solutions
Jong Il Park, Hwa Young Lee, Hyunah Kim, Jisan Lee, Jiwon Shinn, Hun-Sung Kim
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - A head‐to‐head comparison of personal and professional continuous glucose monitoring systems in people with type 1 diabetes: Hypoglycaemia remains the weak spot
Othmar Moser, Marlene Pandis, Felix Aberer, Harald Kojzar, Daniel Hochfellner, Hesham Elsayed, Melanie Motschnig, Thomas Augustin, Philipp Kreuzer, Thomas R. Pieber, Harald Sourij, Julia K. Mader
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2019; 21(4): 1043. CrossRef - Glucose monitoring in diabetes: from clinical studies to real‐world practice
Rebecca C Sagar, Afroze Abbas, Ramzi Ajjan
Practical Diabetes.2019; 36(2): 57. CrossRef - The Effectiveness of Continuous Glucose Monitoring in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review of Literature and Meta-analysis
Cindy Park, Quang A. Le
Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics.2018; 20(9): 613. CrossRef - Effects of Dapagliflozin on 24-Hour Glycemic Control in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Robert R. Henry, Poul Strange, Rong Zhou, Jeremy Pettus, Leon Shi, Sergey B. Zhuplatov, Traci Mansfield, David Klein, Arie Katz
Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics.2018; 20(11): 715. CrossRef - Clinical and economic benefits of professional CGM among people with type 2 diabetes in the United States: analysis of claims and lab data
Joseph A. Sierra, Mona Shah, Max S. Gill, Zachery Flores, Hiten Chawla, Francine R. Kaufman, Robert Vigersky
Journal of Medical Economics.2018; 21(3): 225. CrossRef - Role of continuous glucose monitoring for type 2 in diabetes management and research
Robert Vigersky, Maneesh Shrivastav
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2017; 31(1): 280. CrossRef - Assessing the Therapeutic Utility of Professional Continuous Glucose Monitoring in Type 2 Diabetes Across Various Therapies: A Retrospective Evaluation
Jothydev Kesavadev, Robert Vigersky, John Shin, Pradeep Babu Sadasivan Pillai, Arun Shankar, Geethu Sanal, Gopika Krishnan, Sunitha Jothydev
Advances in Therapy.2017; 34(8): 1918. CrossRef - Use of Continuous Glucose Monitoring in Youth-Onset Type 2 Diabetes
Christine L. Chan
Current Diabetes Reports.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - The efficacy and safety of adding either vildagliptin or glimepiride to ongoing metformin therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Gyuri Kim, Sewon Oh, Sang-Man Jin, Kyu Yeon Hur, Jae Hyeon Kim, Moon-Kyu Lee
Expert Opinion on Pharmacotherapy.2017; 18(12): 1179. CrossRef - Morning Spot Urine Glucose-to-Creatinine Ratios Predict Overnight Urinary Glucose Excretion in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes
So Ra Kim, Yong-ho Lee, Sang-Guk Lee, Sun Hee Lee, Eun Seok Kang, Bong-Soo Cha, Hyun Chul Lee, Jeong-Ho Kim, Byung-Wan Lee
Annals of Laboratory Medicine.2017; 37(1): 9. CrossRef - The Contemporary Role of Masked Continuous Glucose Monitoring in a Real-Time World
Ian Blumer
Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology.2016; 10(3): 790. CrossRef - Glycemic Variability: How Do We Measure It and Why Is It Important?
Sunghwan Suh, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2015; 39(4): 273. CrossRef
- Biological and Clinical Impacts of Glucose Metabolism in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma
- Pattern of Stress-Induced Hyperglycemia according to Type of Diabetes: A Predator Stress Model
- Jin-Sun Chang, Young-Hye You, Shin-Young Park, Ji-Won Kim, Hun-Sung Kim, Kun-Ho Yoon, Jae-Hyoung Cho
- Diabetes Metab J. 2013;37(6):475-483. Published online December 12, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2013.37.6.475
- 4,051 View
- 50 Download
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background We aimed to quantify stress-induced hyperglycemia and differentiate the glucose response between normal animals and those with diabetes. We also examined the pattern in glucose fluctuation induced by stress according to type of diabetes.
Methods To load psychological stress on animal models, we used a predator stress model by exposing rats to a cat for 60 minutes and measured glucose level from the beginning to the end of the test to monitor glucose fluctuation. We induced type 1 diabetes model (T1D) for ten Sprague-Dawley rats using streptozotocin and used five Otsuka Long-Evans Tokushima Fatty rats as obese type 2 diabetes model (OT2D) and 10 Goto-Kakizaki rats as nonobese type 2 diabetes model (NOT2D). We performed the stress loading test in both the normal and diabetic states and compared patterns of glucose fluctuation among the three models. We classified the pattern of glucose fluctuation into A, B, and C types according to speed of change in glucose level.
Results Increase in glucose, total amount of hyperglycemic exposure, time of stress-induced hyperglycemia, and speed of glucose increase were significantly increased in all models compared to the normal state. While the early increase in glucose after exposure to stress was higher in T1D and NOT2D, it was slower in OT2D. The rate of speed of the decrease in glucose level was highest in NOT2D and lowest in OT2D.
Conclusion The diabetic state was more vulnerable to stress compared to the normal state in all models, and the pattern of glucose fluctuation differed among the three types of diabetes. The study provides basic evidence for stress-induced hyperglycemia patterns and characteristics used for the management of diabetes patients.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Stress hyperglycemia as first sign of asymptomatic type 1 diabetes: an instructive case
Wei-De Wang, Chun-Hao Chu, Chiung-Hsi Tien, Shuo-Yu Wang, Shih-Yao Liu, Chien-Ming Lin
BMC Pediatrics.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Genetic determinants of obesity heterogeneity in type II diabetes
Somayeh Alsadat Hosseini Khorami, Mohd Sokhini Abd Mutalib, Mohammad Feili Shiraz, Joseph Anthony Abdullah, Zulida Rejali, Razana Mohd Ali, Huzwah Khaza’ai
Nutrition & Metabolism.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Sex Dimorphic Responses of the Hypothalamus–Pituitary–Thyroid Axis to Maternal Separation and Palatable Diet
Lorraine Jaimes-Hoy, Fidelia Romero, Jean-Louis Charli, Patricia Joseph-Bravo
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Hesperidin protects against stress induced gastric ulcer through regulation of peroxisome proliferator activator receptor gamma in diabetic rats
Shimaa M. Elshazly, Dalia M. Abd El Motteleb, Islam A.A.E-H. Ibrahim
Chemico-Biological Interactions.2018; 291: 153. CrossRef - Physiology and Neurobiology of Stress and the Implications for Physical Health
B Sivaprakash
Annals of SBV.2014; 3(1): 25. CrossRef
- Stress hyperglycemia as first sign of asymptomatic type 1 diabetes: an instructive case
- Education as Prescription for Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Compliance and Efficacy in Clinical Practice
- Mi Yeon Kim, Sunghwan Suh, Sang-Man Jin, Se Won Kim, Ji Cheol Bae, Kyu Yeon Hur, Sung Hye Kim, Mi Yong Rha, Young Yun Cho, Myung-Shik Lee, Moon Kyu Lee, Kwang-Won Kim, Jae Hyeon Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2012;36(6):452-459. Published online December 12, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2012.36.6.452
- 4,413 View
- 33 Download
- 12 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Diabetes self-management education has an important role in diabetes management. The efficacy of education has been proven in several randomized trials. However, the status of diabetes education programs in real Korean clinical practice has not yet been evaluated in terms of patient compliance with the education prescription.
Methods We retrospectively analyzed clinical and laboratory data from all patients who were ordered to undergo diabetes education during 2009 at Samsung Medical Center, Seoul, Korea (
n =2,291). After excluding ineligible subjects, 588 patients were included in the analysis.Results Among the 588 patients, 433 received education. The overall compliance rate was 73.6%, which was significantly higher in the subjects with a short duration or living in a rural area compared to those with a long duration (85.0% vs. 65.1%, respectively;
P <0.001) or living in an urban area (78.2% vs. 70.4%, respectively;P =0.037). The hemoglobin A1c decreased greater in the compliant group (from 7.84±1.54 at baseline to 6.79±1.06 at 3 months and 6.97±1.20 at 12 months after prescription in the compliant group vs. from 7.74±1.25 to 7.14±1.02 and 7.24±1.24 in the non-compliant group;P =0.001). The decrease in hemoglobin A1c was greater in the subjects with a short duration (P =0.032).Conclusion In our study a large percent of patients refuse to get education despite having a prescription from their physician. This refusal rate was higher in the patients with long-standing diabetes or in urban residence. Furthermore, education was more effective in patients with a short duration of diabetes in clinical practice.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Clinical Effects of a Home Care Pilot Program for Patients with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus: A Retrospective Cohort Study
Sejeong Lee, KyungYi Kim, Ji Eun Kim, Yura Hyun, Minyoung Lee, Myung-Il Hahm, Sang Gyu Lee, Eun Seok Kang
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(5): 693. CrossRef - Management Status of Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus at General Hospitals in Korea: A 5-Year Follow-Up Study
Jin Hee Jung, Jung Hwa Lee, Hyang Mi Jang, Young Na, Hee Sun Choi, Yeon Hee Lee, Yang Gyo Kang, Na Rae Kim, Jeong Rim Lee, Bok Rye Song, Kang Hee Sim
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2022; 23(1): 64. CrossRef - The Effectiveness of Multidisciplinary Team-Based Education in the Management of Type 2 Diabetes
Jong Ho Kim, Yun Jeong Nam, Won Jin Kim, Kyung Ah Lee, A Ran Baek, Jung Nam Park, Jin Mi Kim, Seo Young Oh, Eun Heui Kim, Min Jin Lee, Yun Kyung Jeon, Bo Hyun Kim, In Joo Kim, Yong Ki Kim, Sang Soo Kim
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2018; 19(2): 119. CrossRef - The diabetes self-management educational programs and their integration in the usual care: A systematic literature review
Emmanuel Kumah, Giulia Sciolli, Maria Laura Toraldo, Anna Maria Murante
Health Policy.2018; 122(8): 866. CrossRef - Diabetes Camp as Continuing Education for Diabetes Self-Management in Middle-Aged and Elderly People with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
So Young Park, Sun Young Kim, Hye Mi Lee, Kyu Yeon Hur, Jae Hyeon Kim, Moon-Kyu Lee, Kang-Hee Sim, Sang-Man Jin
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2017; 41(2): 99. CrossRef - Educational attainment moderates the associations of diabetes education with health outcomes
Su Hyun Kim
International Journal of Nursing Practice.2016; 22(5): 444. CrossRef - Experiences of Diabetes Education among Educators of Diabetes : a content analysis approach
Soo Jin Kang, Soo Jung Chang
Journal of Korean Public Health Nursing.2016; 30(2): 221. CrossRef - Barrier Factors to the Completion of Diabetes Education in Korean Diabetic Adult Patients: Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys 2007-2012
Hee-Tae Kim, Kiheon Lee, Se Young Jung, Seung-Min Oh, Su-Min Jeong, Yoon-Jung Choi
Korean Journal of Family Medicine.2015; 36(5): 203. CrossRef -
Determinants of glycaemic control in a practice setting: the role of weight loss and treatment adherence (The
DELTA
Study)
C. McAdam‐Marx, B. K. Bellows, S. Unni, J. Mukherjee, G. Wygant, U. Iloeje, J. N. Liberman, X. Ye, F. J. Bloom, D. I. Brixner
International Journal of Clinical Practice.2014; 68(11): 1309. CrossRef - Health education via mobile text messaging for glycemic control in adults with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Mohsen Saffari, Ghader Ghanizadeh, Harold G. Koenig
Primary Care Diabetes.2014; 8(4): 275. CrossRef - The Appropriateness of the Length of Insulin Needles Based on Determination of Skin and Subcutaneous Fat Thickness in the Abdomen and Upper Arm in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
Kang Hee Sim, Moon Sook Hwang, Sun Young Kim, Hye Mi Lee, Ji Yeun Chang, Moon Kyu Lee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2014; 38(2): 120. CrossRef - Diabetes Attitudes, Wishes and Needs second study (DAWN2™): Cross‐national benchmarking of diabetes‐related psychosocial outcomes for people with diabetes
A. Nicolucci, K. Kovacs Burns, R. I. G. Holt, M. Comaschi, N. Hermanns, H. Ishii, A. Kokoszka, F. Pouwer, S. E. Skovlund, H. Stuckey, I. Tarkun, M. Vallis, J. Wens, M. Peyrot
Diabetic Medicine.2013; 30(7): 767. CrossRef
- Clinical Effects of a Home Care Pilot Program for Patients with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus: A Retrospective Cohort Study

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





